Electricity is a major and rising expense for most businesses so getting a good deal is imperative. But how can you tell if your deal is good, average or highway robbery when your bill is a dense jumble of numbers and terms that seems designed to confuse? How can you understand how your business energy bill is calculated if invoices seem so complex?
Exhibit A.
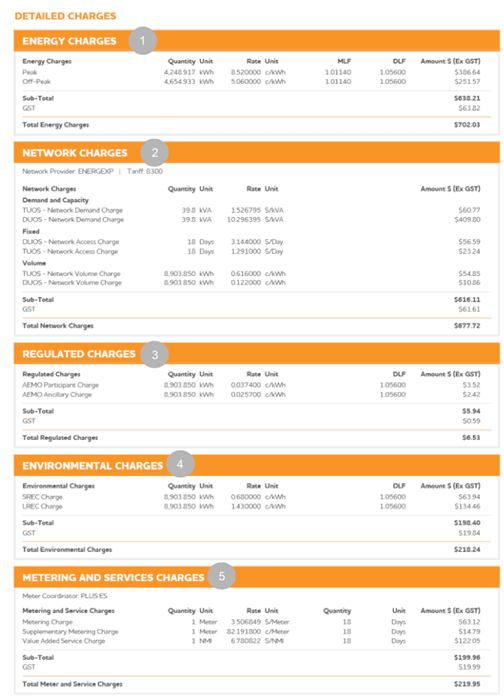
Complex pricing structures make it difficult to tell if you are on the right plan, compare offers from different providers and spot billing errors. Problems that can add up to big and unnecessary expenses for your business.
But fear not.
Here is a quick guide to the components that make up your business energy bill.
1. Energy Charges
Well OK, this one’s kind of obvious. This is what you signed up for – the electricity you need to power your business. These charges usually comprise around 50% of your bill and are calculated by multiplying your consumption (in kWh) by your rate (in cents).
Simple right?
Not really. Rates are commonly split into ‘time of use’ prices that reflect demand. This means to choose the right plan you need to understand some characteristics of your business’ usage. When do you typically require the most energy? Is any of your load flexible? Could you shift some activities to off-peak times? Things get trickier if you are generating solar on-site and need to weigh the solar buyback rate against your consumption costs.
The truth is your business is unique and there is no easy way to find the optimal plan. At Leading Edge Energy we can guide you through this process and ensure you are getting the best deal.
2. Network Charges
Network charges rival energy charges for making up the largest portion of your bill and is one of the main areas where costs can be reduced. Network charges are paid to the transmission and distribution companies and cover the ‘poles and wires’ that carry electrons to your premises. These tariffs are complicated and include daily fixed network access charges, time of use charges applied per kWh and demand charges.
Demand charges can be calculated a number of ways but in a nutshell, they relate to your business’ highest 30-minute interval of demand within a given period and are measured in kilo-volt-amperes (kVA). If you want to know what a kVA is and you’ve been waiting since high school for an opportunity to finally actually use Pythagoras Theorem then you’ll find everything you need on the Power Triangle and Power Factor here. But the important thing to know is that kVA measures the power you use as well as some that you don’t and can be affected by your equipment.
Leading Edge Energy can conduct a detailed network tariff analysis to ensure you are getting the best deal and help you identify strategies to reduce your demand charges.
3. Regulated Charges
Participant Charge
Thanks for coming! That will be 0.0374c/kWh, thanks.
What exactly are you participating in? This charge is paid to the Australian Electricity Market Operator (AEMO) to cover costs associated with running the National Electricity Market (NEM). The NEM is busy matching electricity supply and demand across one of the largest interconnected power systems in the world. In real-time. 24/7. It’s a big job and the costs are distributed across all market participants.
The participant charge is a fixed rate applied per kWh and is updated by AEMO yearly.
Ancillary Services
Ancillary services are support services that AEMO has to purchase from generators to keep the whole system happy. Power grids are sensitive beasts and the frequency in all those wires needs to be kept within a tight band around 50 Hertz (between 49.85 and 50.15Hz to be exact). In Q1 2019 AEMO spent $36.5 million maintaining system frequency and these costs are passed on to all users. Ancillary service charges are updated monthly and trending downwards.
4. Environmental Charges
There is a range of Federal and State schemes that affect your energy bill. The Large Scale Renewable Energy Target (LRET) and Small Scale Renewable Energy Scheme (SRES) oblige retailers to purchase renewable energy certificates that correspond to renewable energy generation. These costs are passed on to consumers at a per kWh rate determined by the price of certificates. Since the target of 20% renewable energy by 2020 has been met certificate prices are trending strongly downwards.
5. Metering and Services Charges
Meter Charge
The meter charge covers the cost of installing, maintaining and reading your meter. Newer smart meters are more expensive to install but can deliver savings by displacing the need for field technicians. Meter charges are fixed costs that are applied to your bill at a daily rate.
Retail Supply Charge
This is the part your retailer keeps to cover the cost of administering your account. Everything from the electricity traders that purchased your power in the wholesale electricity markets to the envelope that your bill arrived in is contained in this price.
So there you have it.
Your business energy bill is a complex mix of fixed and variable costs that you have varying degrees of control over. If you would like to take control of your electricity bill give us a call at Leading Edge Energy and let our experts guide you through the process.
Still confused about your business energy bill?
Leading Edge Energy, your people in power, are always ready to help businesses like yours know what type of energy contract they’re on, if they’re being overcharged, and what to do when they experience bill shock.
Contact us at 1300-852-770 or e-mail us at hello@leadingedgeenergy.com.au to learn more about your energy bills. Best of all, as energy brokers in Australia, we can also guide your business on the way to energy efficiency and cost reduction. Take control of your business’ energy bills!













